


 Français
Français


At hatch, the digestive tracts of broilers can be rapidly colonized by microorganisms from the surrounding environment. Because younger birds have fewer bacterial species in the intestinal tract than adults, their gut is more susceptible to disorders promoted by harmful bacteria (CHR Hanson, 2020). The poultry industry is moving away from the preventative use of antibiotic growth promoters. Therefore, the need to evaluate possible alternatives to promote a healthy gut is becoming increasingly important. One alternative that is being evaluated is the use of probiotics as these organisms have been shown to have a positive impact on gut health. There are several methods of delivering the probiotics to the birds. The most common is by in-feed delivery. However, there is evidence that during the heat treatment of the feed, the probiotic can become inactive (Ducatelle et al., 2014). The efficacy of in-water delivery depends on the precision of the chick watering devices and there is a potential risk for water quality issues. In ovo technology involves the direct inoculation of bioactive substances directly to the developing embryo and may address some of the limitations of the other delivery methods.
To evaluate the effect of delivery route (in-water vs. in-feed vs. in ovo) of a probiotic product (Bacillus subtilis fermentation extract) on growth performance, intestinal morphology, cecal short-chain fatty acid concentration, and cecal microbiota in broiler chickens.
The results from this trial indicates that the use of the probiotic, Bacillus subtilis, has potential to improve gut health and gut structure without negatively impacting growth performance. This could be an important tool in the toolbox of producers as they move towards the elimination of the use of preventative antibiotics.
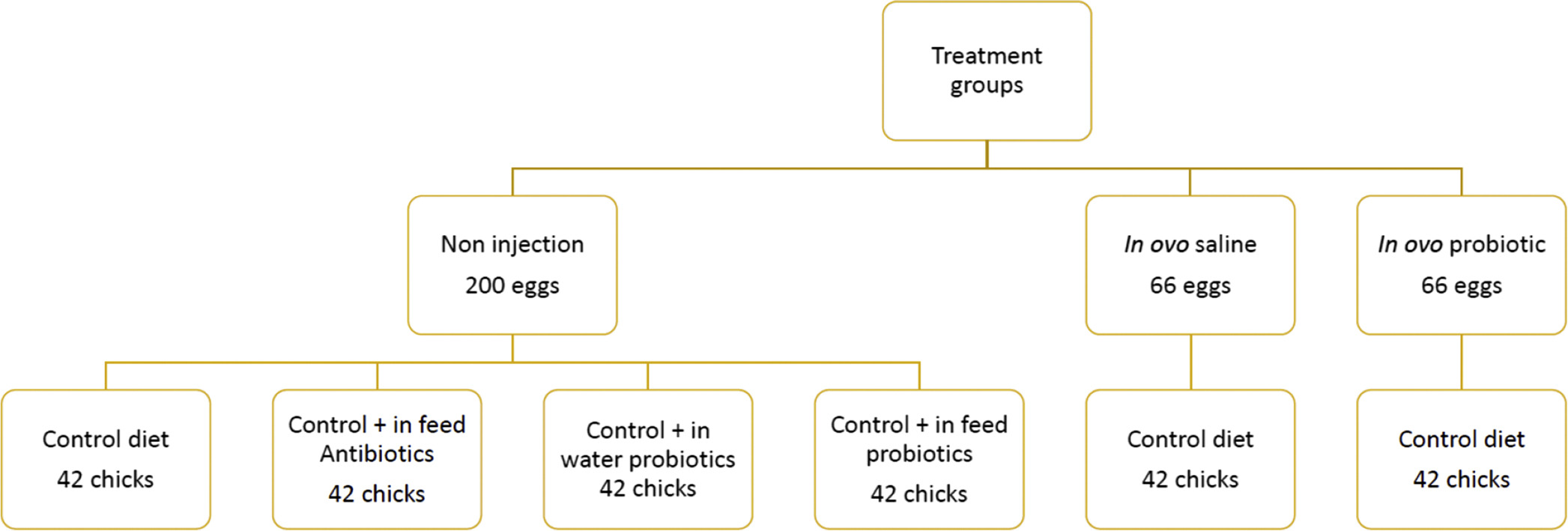
A total of 450 fertile eggs sourced from Cobb 500 broiler breeders were arranged in 6 replicate trays inside an incubator with each tray containing 75 eggs. On day 18.5 of incubation, eggs were randomly allocated to 3 experimental groups. Sixty-six eggs in the in ovo probiotic group had the probiotic, Bacillus subtilis injected into the amnion; an additional 66 eggs were injected with saline solution using the same injection method for the in ovo saline group. The control group consisted of 200 non-injected eggs. On day 21, unhatched eggs were counted and opened to check for the stage of embryo death. The remaining hatched chicks were weighed and navel quality was evaluated. The non-injection chicks were randomly re-allocated to one of four treatment groups with 42 birds per group: in-feed antibiotics (Bacitracin), in-water probiotic, in-feed probiotic, and control (CTRL; Corn-wheat-soybean diet). These 4 treatments were added to the treatment groups of in ovo probiotic and in ovo saline to make a total of 6 treatment groups. The birds were housed in 6 replicate cages per treatment with 7 birds per cage and raised for 28 days. Growth performance, feed intake and average body weight were measured on days 7, 14, 21 and 28. This data was used to calculate daily feed intake, average daily gain and feed conversion ratio. On day 28, two birds per pen were randomly selected and euthanized. Gut tissue samples were collected for short-chain fatty acid analyses, incidence of necrotic enteritis and intestinal morphology measurements.
CHR Hanson, 2020. https://www.chr-hansen.com/en/animal-health/cards/article-cards/poultry/mar18-gut-health-matters
Ducatelle et al., 2014. A review on prebiotics and probiotics for the control of dysbiosis: Present status and future perspectives. Animal 9:43–48.
Researchers
Samson Oladokun, Alyssa Koehler, Janice MacIsaac, Eveline M. Ibeagha-Awemu, and Deborah I. Adewole
Funding
Canadian Agricultural Partnership – Advancing Agricultural Research and Innovation Initiative, Chicken Farmers of Nova Scotia, Dalhousie University
The full publication of this work can be found online.
Adapted from the Atlantic Poultry Research Institute’s Factsheets
PO Box 550 Truro, NS B2N 5E3 (902) 893-6657
Laurie.Eagles@dal.ca www.APRinstitute.ca

